
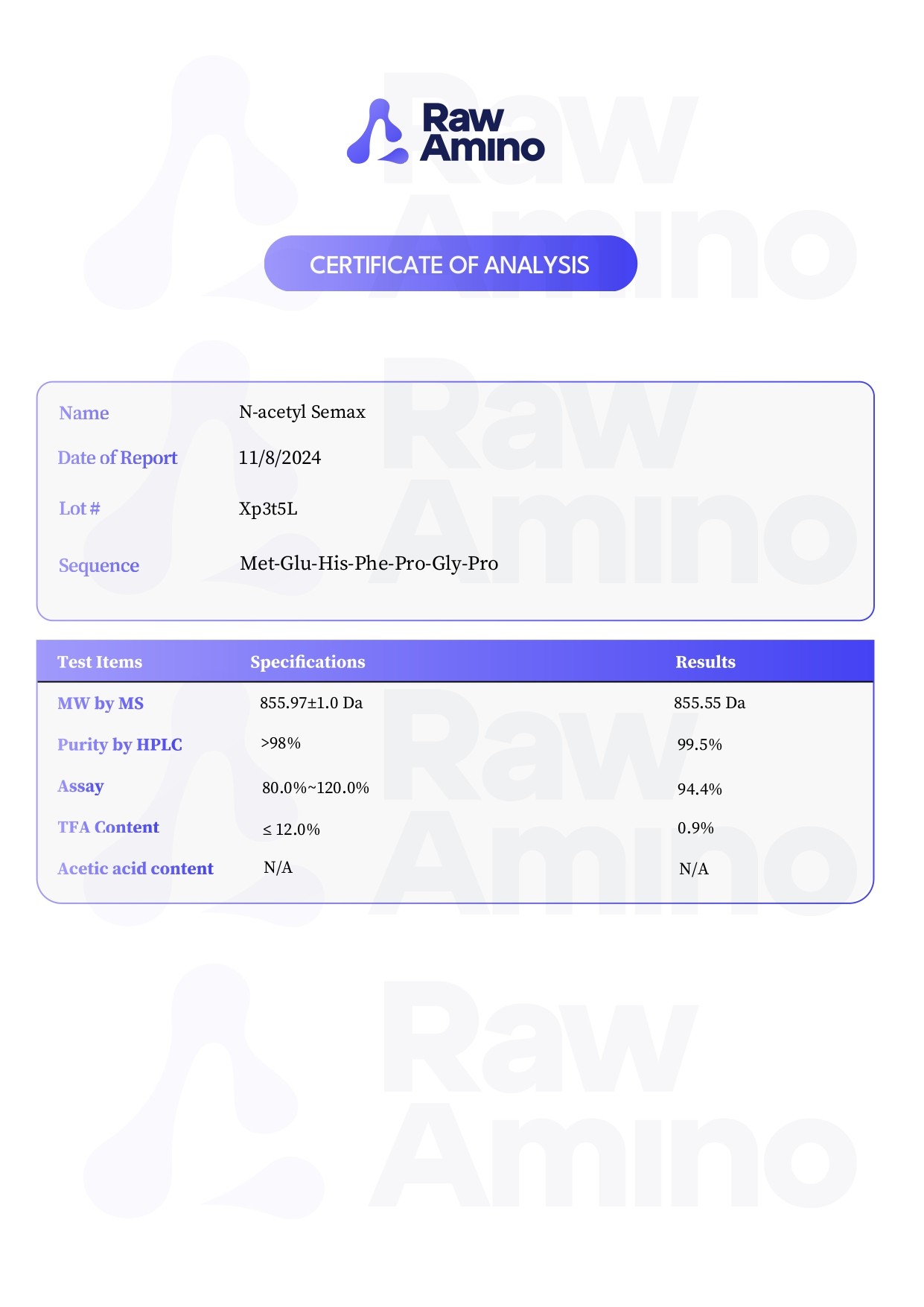
N-Acetyl Semax – 25MG
$58.00
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 8 | 5% | $55.10 |
| 9 + | 10% | $52.20 |
Scientific Overview of N-Acetyl Semax
N-Acetyl Semax is considered a modified form of the Semax peptide, itself derived from fragments of melanocortin-related hormones such as adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). The modification involves acetylation at the N-terminus, as well as the inclusion of a Pro-Gly-Pro (PGP) motif at the C-terminus. Researchers suggest that these changes may enhance the peptide’s stability, alter its interactions with enzymes, and potentially influence how it traverses cellular barriers such as the blood-brain barrier. Acetylation has also been observed to reduce affinity for certain metal ions and to contribute to greater resistance against enzymatic breakdown. Collectively, these alterations may contribute to extended experimental persistence of the peptide in laboratory settings.
Alternative Names: Acetyl-Semax, Ac-Semax, N-Ac-Semax
N-Acetyl Semax Studies and Research Data
Neural Signaling Pathways and Cognitive Research
Studies exploring Semax indicate potential influences on neural pathways associated with cognition. Reports describe enhanced performance in memory recall tasks and higher activity in brain regions linked to attention and learning. Imaging-based studies further suggest altered activation patterns within resting-state networks, leading researchers to hypothesize that Semax—and by extension, N-Acetyl Semax—may play a role in modulating large-scale neuronal connectivity.
Neurotrophic Factor Regulation
A key area of focus involves the relationship between Semax peptides and neurotrophic proteins, particularly Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF). Experimental models point to elevated hippocampal BDNF protein levels following exposure, alongside increases in trkB receptor activity. These outcomes may indicate transcriptional regulation of neurotrophic genes and pathways, with certain findings suggesting region-specific actions. Some reports extend these discussions to potential implications in ischemia-related experimental models, where correlations between peptide exposure and BDNF signaling have been noted.
Neurochemical Systems: Serotonin, Dopamine, and Enkephalins
Evidence also suggests that Semax may interact with major neurotransmitter systems. Experimental data point to possible modulation of serotonergic signaling, reflected in changes in 5-HIAA metabolite levels. Although direct dopamine levels do not appear to shift significantly, responsiveness to dopaminergic modulators may be altered. Additional investigations indicate that Semax may inhibit enzymes responsible for degrading enkephalins, possibly leading to broader changes across neurotransmitter systems, including those involving serotonin and dopamine. These findings remain preliminary and open to further research.
Inflammatory and Cellular Stress Pathways
Another area of investigation relates to potential modulation of cellular pathways involved in inflammation, stress responses, and ischemia. Studies describe observed downregulation of proteins linked to neuroinflammation, such as c-Fos and JNK, while also noting upregulation of CREB in subcortical regions. Researchers propose that these interactions may represent compensatory mechanisms that could hypothetically influence recovery processes in laboratory ischemia models. Observations appear to be region-specific, with distinct differences noted between cortical and subcortical responses.
N-Acetyl Semax and Gastrointestinal Research
Beyond neurobiology, Semax peptides have also been studied in relation to digestive tissues. Reports suggest potential protective or restorative actions in experimental ulcer models. Comparative data indicate faster resolution of ulcers in research groups exposed to Semax compared to controls, though the mechanisms remain uncertain.
Conclusion
The scientific literature surrounding N-Acetyl Semax builds upon extensive investigations of its parent compound, Semax. Emerging findings highlight potential roles in neurochemical signaling, neurotrophic factor regulation, and pathways linked to inflammation and cellular stress. Region-specific responses, variations in neurotransmitter activity, and broader implications for neuronal function have all been suggested. While research continues to expand, many mechanisms remain speculative, and outcomes are not yet fully understood.
References
- Sudarkina OY, Filippenkov IB, Stavchansky VV, Denisova AE, Yuzhakov VV, Sevan'kaeva LE, Valieva LV, Remizova JA, Dmitrieva VG, Gubsky LV, Myasoedov NF, Limborska SA, Dergunova LV. Brain Protein Expression Profile Confirms the Protective Effect of the ACTH(4-7)PGP Peptide (Semax) in a Rat Model of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 8;22(12):6179. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126179. PMID: 34201112; PMCID: PMC8226508.
- Ivanikov, I. O., Brekhova, M. E., Samonina, G. E., Myasoedov, N. F., & Ashmarin, I. P. (2002). Therapy of peptic ulcer with semax peptide. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 134(1), 73–74. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1020621124776
- Gusev, E. I., Martynov, M. Y., Kostenko, E. V., Petrova, L. V., & Bobyreva, S. N. (2018). Éffektivnost’ semaksa pri lechenii bol’nykh na raznykh stadiiakh ishemicheskogo insul’ta. Zhurnal nevrologii i psikhiatrii imeni S.S. Korsakova, 118(3. Vyp. 2), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.17116/jnevro20181183261-68
- Magrì, A., Tabbì, G., Giuffrida, A., Pappalardo, G., Satriano, C., Naletova, I., Nicoletti, V. G., & Attanasio, F. (2016). Influence of the N-terminus acetylation of Semax, a synthetic analog of ACTH(4-10), on copper(II) and zinc(II) coordination and biological properties. Journal of inorganic biochemistry, 164, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.08.013
- Nataliya Yu. Glazova, Daria M. Manchenko, Maria A. Volodina, Svetlana A. Merchieva, Ludmila A. Andreeva, Vladimir S. Kudrin, Nikolai F. Myasoedov, Natalia G. Levitskaya. (2021). Semax, synthetic ACTH(4–10) analogue, attenuates behavioural and neurochemical alterations following early-life fluvoxamine exposure in white rats. Neuropeptides, 86, 102114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2020.102114
- Eremin KO, Kudrin VS, Saransaari P, Oja SS, Grivennikov IA, Myasoedov NF, Rayevsky KS. (2005). Semax, an ACTH(4-10) analogue with nootropic properties, activates dopaminergic and serotoninergic brain systems in rodents. Neurochem Res, 30(12):1493-500. doi: 10.1007/s11064-005-8826-8.
- Kurysheva, N. I., Shpak, A. A., Ioĭleva, E. E., Galanter, L. I., Nagornova, N. D., Shubina, N. I.u, & Shlyshalova, N. N. (2001). Semax in the treatment of glaucomatous optic neuropathy in patients with normalized ophthalmic tone. Vestnik oftalmologii, 117(4), 5–8.
- Dolotov OV, Karpenko EA, Inozemtseva LS, Seredenina TS, Levitskaya NG, Rozyczka J, Dubynina EV, Novosadova EV, Andreeva LA, Alfeeva LY, Kamensky AA, Grivennikov IA, Myasoedov NF, Engele J. (2006). Semax, an analog of ACTH(4-10) with cognitive effects, regulates BDNF and trkB expression in the rat hippocampus. Brain Res, 1117(1):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.108.
- Kaplan, A. Y. A., Kochetova, A. G., Nezavibathko, V. N., Rjasina, T. V., & Ashmarin, I. P. (1996). Synthetic acth analogue semax displays nootropic‐like activity in humans. Neuroscience Research Communications, 19(2), 115-123.
- Kost NV, Sokolov OIu, Gabaeva MV, Grivennikov IA, Andreeva LA, Miasoedov NF, Zozulia AA. (2001). Semax and selank inhibit the enkephalin-degrading enzymes from human serum. Bioorg Khim. 27(3):180-3. doi: 10.1023/a:1011373002885.
Disclaimer:
The products mentioned are intended solely for laboratory research and in-vitro experimentation. They are not approved for human or animal use of any kind. All details provided are for educational purposes only. By purchasing from this site, you agree to comply with our Terms and Conditions.


9 reviews for N-Acetyl Semax – 25MG
Only logged in customers may leave a review.





ythomas –
proto734k –
patricia32 –
ion777z –
patrick12 –
tyler85 –
nicholas_garza –
patrick223 –
Jill Y. –