
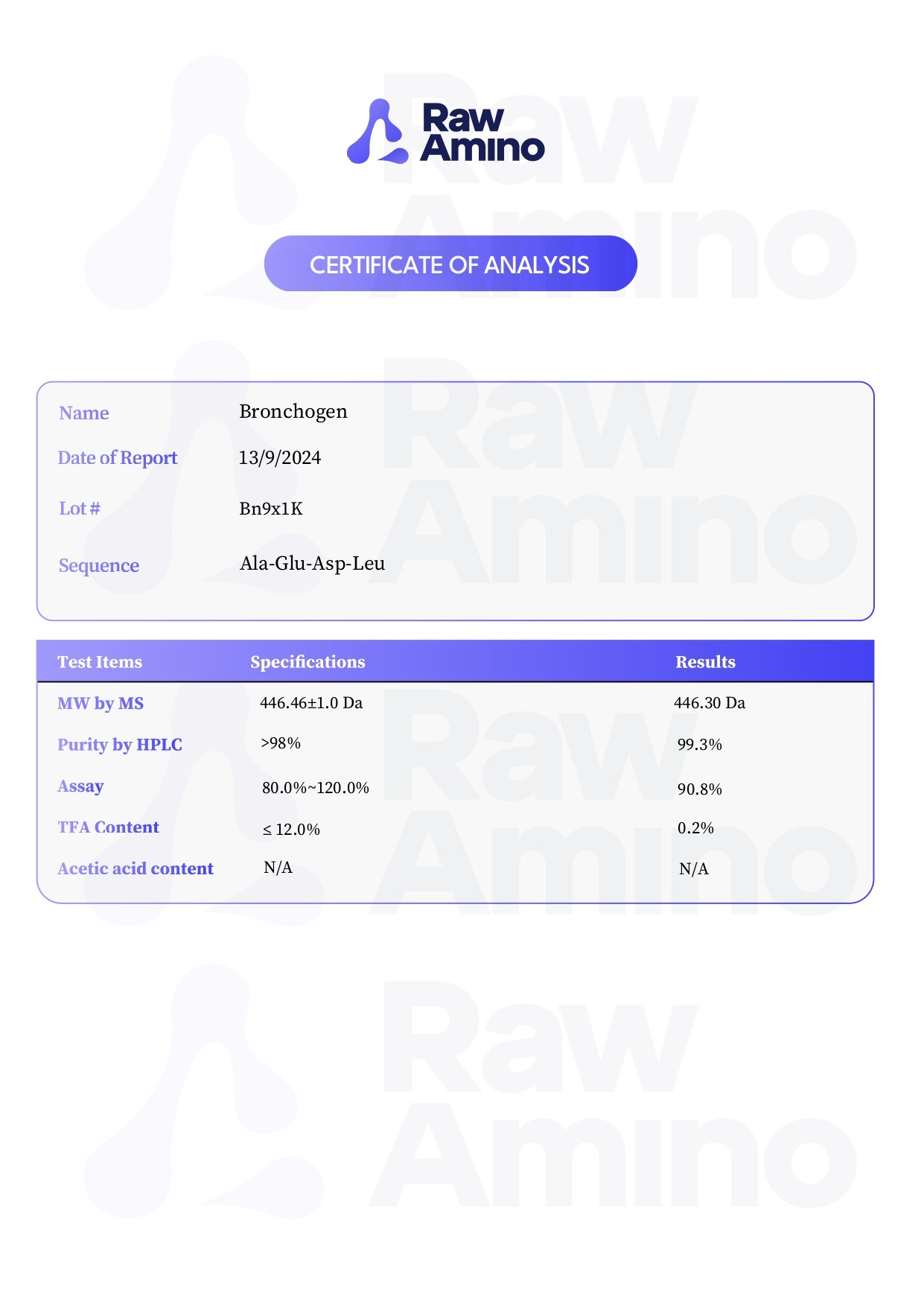
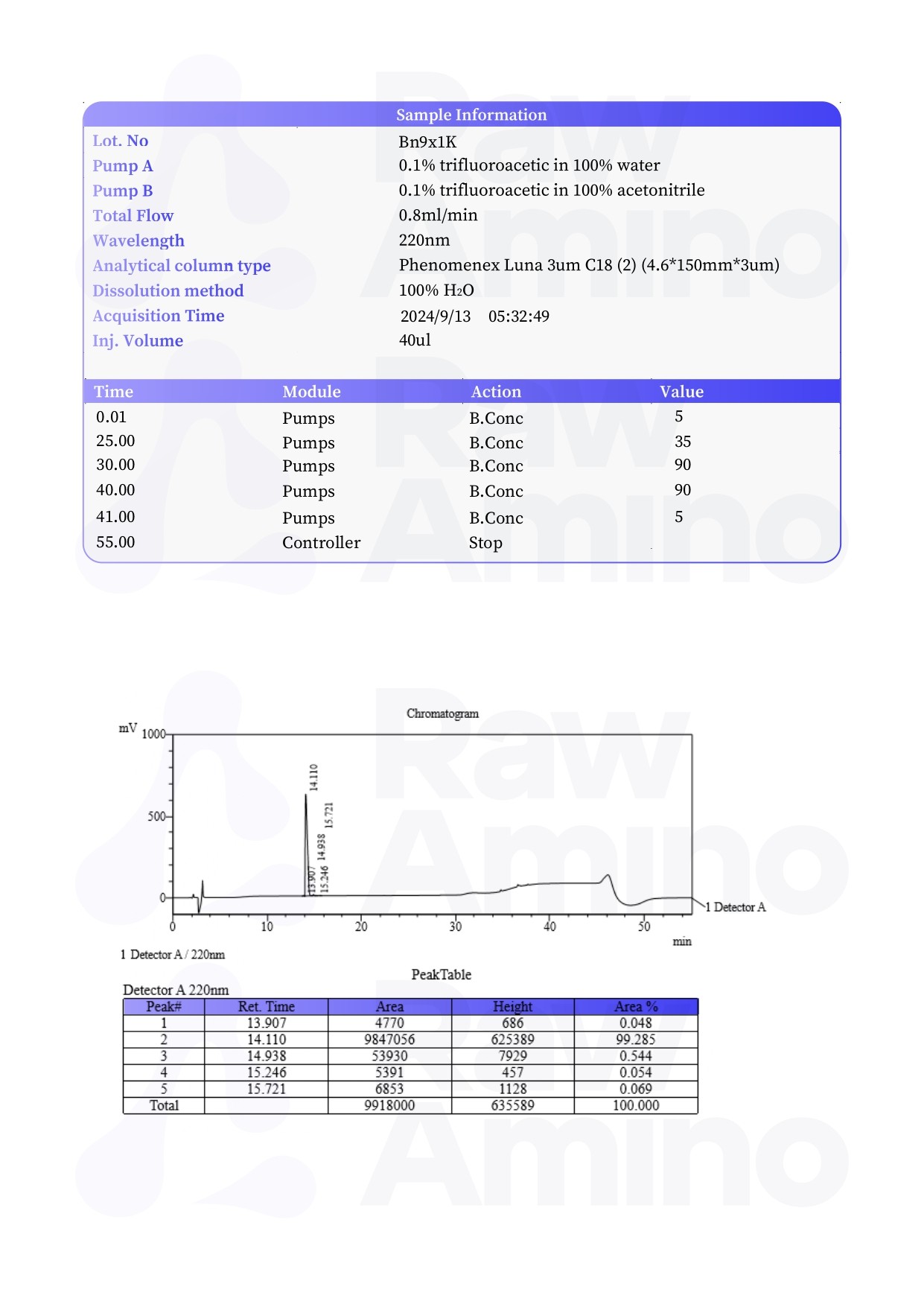
Bronchogen – 20MG
$64.00
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 8 | 5% | $60.80 |
| 9 + | 10% | $57.60 |
Scientific Overview of Bronchogen
Bronchogen, also referred to as AEDL, is part of the group often described as Khavinson peptides. These are short regulatory peptides that have been proposed to interact with nuclear components and genetic material. Research suggests that Bronchogen may show an affinity for processes linked to respiratory tissues, with hypotheses pointing toward its potential involvement in regulating transcription factors and influencing molecular pathways associated with epithelial integrity.
Alternative Names: AEDL
Bronchogen Studies and Research Data
Investigations into DNA Stabilization
Experimental findings indicate that Bronchogen may interact with DNA in ways that alter its thermodynamic behavior. In certain laboratory models, the peptide appeared to raise the thermal stability of DNA by several degrees, with researchers suggesting non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding or van der Waals forces as possible explanations. These proposed stabilizing actions could be relevant for understanding the peptide’s potential role in modulating nucleic acid structures, though the precise mechanisms remain under investigation.
Bronchogen Research on Inflammatory Models
Some animal studies have explored the potential of Bronchogen in modulating inflammatory activity associated with airway injury. Reports propose that it may influence neutrophilic infiltration, epithelial barrier characteristics, and the balance of cytokines within respiratory tissues. Observations include changes in markers linked to immune and structural responses, suggesting possible pathways by which Bronchogen might interact with inflammation-related processes.
Bronchogen Studies on Cellular Renewal
Bronchogen has been examined in research focused on cellular regeneration, particularly within bronchial epithelial models. Findings suggest the peptide may engage with DNA without disrupting the helical structure, potentially influencing cellular activity and renewal processes. Investigators have speculated that such interactions might hold promise for studies in targeted gene-related regulation and directed molecular delivery systems, though further exploration is needed to clarify mechanisms and outcomes.
Exploration of Genetic Interactions
Scientific investigations propose that Bronchogen may preferentially interact with specific DNA sequences, including regions associated with methylation processes. Such binding could have implications for the regulation of gene activity and differentiation, though evidence remains preliminary. Additional hypotheses have also suggested potential roles in preventing structural remodeling of bronchial tissue in experimental settings.
Conclusion
Research on Bronchogen highlights its potential role as a short regulatory peptide with interactions at the genetic and cellular level. Findings suggest possible involvement in DNA stabilization, modulation of inflammatory responses, and epithelial renewal, though these remain exploratory themes requiring continued investigation.
References
- Morozova, E. A., Lin’kova, N. S., Khavinson, V. K., Soloviev, A. Y., & Kasyanenko, N. A. (2017). In vitro interaction of the AEDL peptide with DNA. Journal of Structural Chemistry, 58, 420–424.
- Khavinson, V. K., Popovich, I. G., Linkova, N. S., Mironova, E. S., & Ilina, A. R. (2021). Peptide Regulation of Gene Expression: A Systematic Review. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 26(22), 7053. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227053
- Monaselidze, J. R., Khavinson, V. K., Gorgoshidze, M. Z., Khachidze, D. G., Lomidze, E. M., Jokhadze, T. A., & Lezhava, T. A. (2011). Effect of the peptide bronchogen (Ala-Asp-Glu-Leu) on DNA thermostability. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 150(3), 375–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1146-x
- Caputi, S., Trubiani, O., Sinjari, B., Trofimova, S., Diomede, F., Linkova, N., Diatlova, A., & Khavinson, V. (2019). Effect of short peptides on neuronal differentiation of stem cells. International journal of immunopathology and pharmacology, 33, 2058738419828613. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058738419828613
- Kuzubova, N. A., Lebedeva, E. S., Dvorakovskaya, I. V., Surkova, E. A., Platonova, I. S., & Titova, O. N. (2015). Modulating Effect of Peptide Therapy on the Morphofunctional State of Bronchial Epithelium in Rats with Obstructive Lung Pathology. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 159(5), 685–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-3047-x
- Fedoreyeva, L. I., Kireev, I. I., Khavinson, V. K., & Vanyushin, B. F. (2011). Penetration of short fluorescence-labeled peptides into the nucleus in HeLa cells and in vitro specific interaction of the peptides with deoxyribooligonucleotides and DNA. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia, 76(11), 1210–1219. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297911110022
- Titova, O. N., Kuzubova, N. A., Lebedeva, E. S., Preobrazhenskaya, T. N., Surkova, E. A., & Dvorakovskaya, I. V. (2017). Rossiiskii fiziologicheskii zhurnal imeni I.M. Sechenova, 103(2), 201–208.
- Khavinson, V. K., Linkova, N. S., Polyakova, V. O., Kheifets, O. V., Tarnovskaya, S. I., & Kvetnoy, I. M. (2012). Peptides tissue-specifically stimulate cell differentiation during their aging. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 153(1), 148–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1664-1
Disclaimer:
The products mentioned are intended solely for laboratory research and in-vitro experimentation. They are not approved for human or animal use of any kind. All details provided are for educational purposes only. By purchasing from this site, you agree to comply with our Terms and Conditions.
Only logged in customers may leave a review.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.