
Cartalax – 20MG
$60.00
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 8 | 5% | $57.00 |
| 9 + | 10% | $54.00 |
Scientific Overview of Cartalax
Cartalax, also referred to as AED or T-31, belongs to the class of short regulatory peptides often discussed in relation to Khavinson’s research. It has been proposed to interact with cellular and genetic pathways linked to tissue regulation and structural maintenance. Investigations suggest it may have relevance for processes associated with cellular aging and the dynamics of connective tissues.
Alternative Names: AED, T-31
Cartalax Studies and Research Data
Explorations in Kidney Models
Experimental studies indicate that Cartalax may play a role in supporting proliferative activity within kidney tissue cultures from both younger and older animal models. Researchers have noted potential influences on the expression of proteins linked with cellular senescence, including observations suggesting possible decreases in markers such as p16, p21, and p53. At the same time, the peptide appears associated with an increase in SIRT-6, a protein often discussed in connection with DNA maintenance. Hypotheses also propose that Cartalax may interact with specific DNA sequences, potentially contributing to observed changes in gene activity in renal cells.
Cartalax Research on Skin Fibroblasts
Investigations into cultured skin fibroblasts suggest Cartalax may influence markers tied to replicative aging. In certain models, the peptide has been associated with apparent changes in Ki-67 expression, a marker commonly linked with cellular renewal. Reports also suggest potential upregulation of CD98hc, which has been connected with regenerative processes. Other findings propose that Cartalax may reduce apoptosis indicators, including caspase activity, and inhibit matrix-degrading enzymes such as MMP-9. Collectively, these themes suggest a possible role in maintaining extracellular structures and delaying some features of cellular decline in fibroblast models.
Studies on Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Cartalax has also been examined in the context of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Research suggests it may modulate gene expression profiles linked with aging in both proliferative and stationary culture phases. Observed changes include a potential upregulation of IGF1 and NFκB, while variations in telomere-related enzymes such as telomerase and tankyrase have also been noted. These findings may point to an involvement of Cartalax in processes tied to genomic stability and cellular signaling.
Cartalax Investigations into Cartilage Pathways
Some recent research has highlighted possible associations between Cartalax and chondrogenic differentiation. Reports suggest the peptide may contribute to pathways linked with cartilage-specific cell development, although these findings remain preliminary and exploratory.
Conclusion
Cartalax has been investigated across several cellular models, with studies suggesting potential influences on fibroblast renewal, kidney tissue dynamics, cartilage pathways, and stem cell gene expression. While findings indicate intriguing molecular interactions, research remains in early stages, and the mechanisms continue to be a subject of exploration.
References
- Ashapkin, V., Khavinson, V., Shilovsky, G., Linkova, N., & Vanuyshin, B. (2020). Gene expression in human mesenchymal stem cell aging cultures: modulation by short peptides. Molecular biology reports, 47(6), 4323–4329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05506-3
- Chalisova, N. I., Lin'kova, N. S., Nichik, T. E., Ryzhak, A. P., Dudkov, A. V., & Ryzhak, G. A. (2015). Peptide Regulation of Cells Renewal Processes in Kidney Tissue Cultures from Young and Old Animals. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 159(1), 124–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-015-2906-9
- Lin'kova, N. S., Drobintseva, A. O., Orlova, O. A., Kuznetsova, E. P., Polyakova, V. O., Kvetnoy, I. M., & Khavinson, V. K. (2016). Peptide Regulation of Skin Fibroblast Functions during Their Aging In Vitro. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 161(1), 175–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3370-x
- Khavinson, V. K., Tarnovskaia, S. I., Lin'kova, N. S., Poliakova, V. O., Durnova, A. O., Nichik, T. E., Kvetnoĭ, I. M., D'iakonov, M. M., & Iakutseni, P. P. (2014). Advances in gerontology = Uspekhi gerontologii, 27(4), 651–656.
- Linkova, N., Khavinson, V., Diatlova, A., Myakisheva, S., & Ryzhak, G. (2023). Peptide Regulation of Chondrogenic Stem Cell Differentiation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(9), 8415.
Disclaimer:
The products mentioned are intended solely for laboratory research and in-vitro experimentation. They are not approved for human or animal use of any kind. All details provided are for educational purposes only. By purchasing from this site, you agree to comply with our Terms and Conditions.

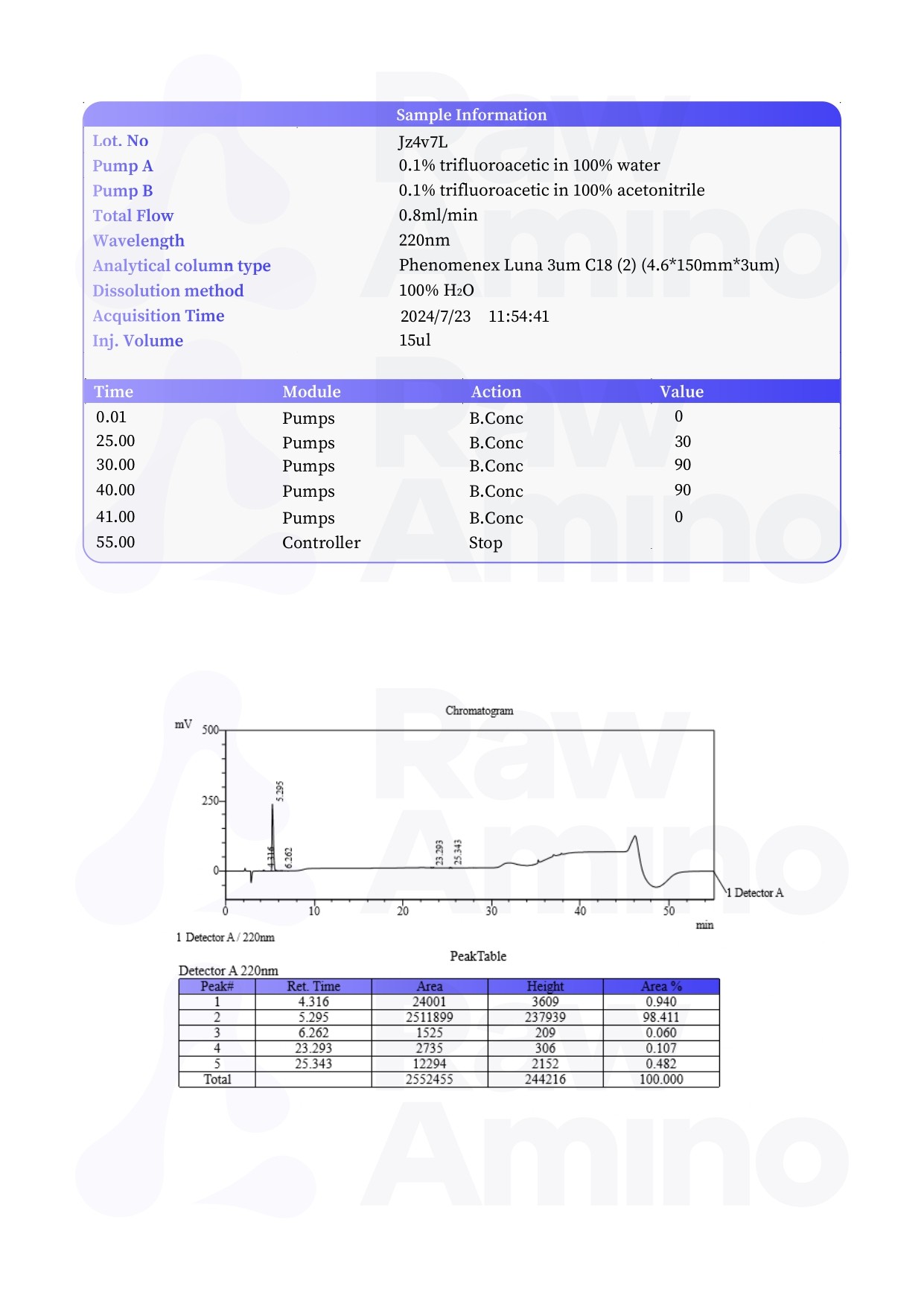

4 reviews for Cartalax – 20MG
Only logged in customers may leave a review.





cmills –
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Top notch experience.
ElizabethS –
The team at Raw Amino was responsive and polite. They explained the COA documents when I asked for clarification and walked me through how the results are verified.
holly654 –
I recently bought peptides from RA. They came highly recommended to me and I can see why. Overall, this turned out better than expected.
holly654 –
Desription is neat. Very informative.