
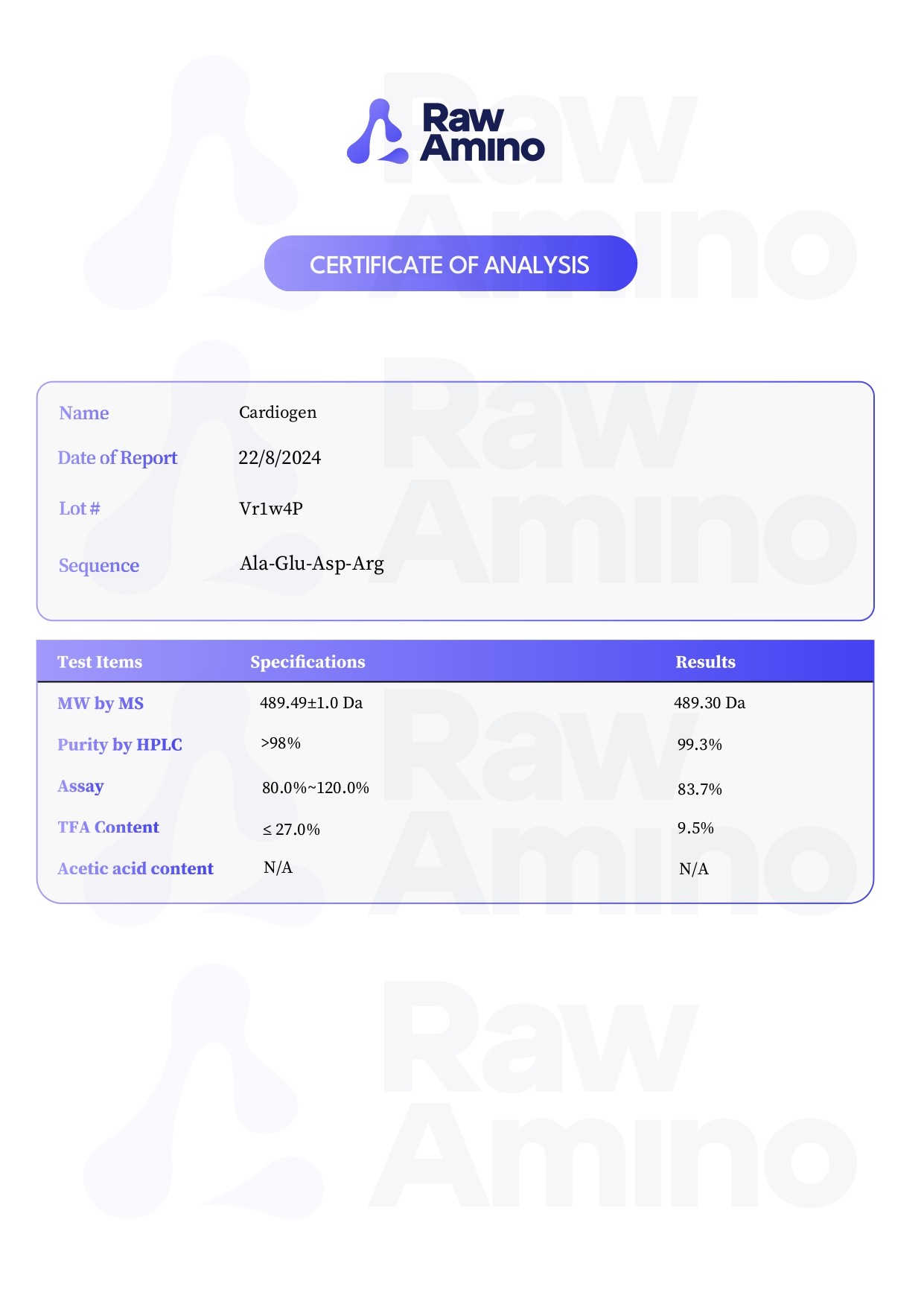
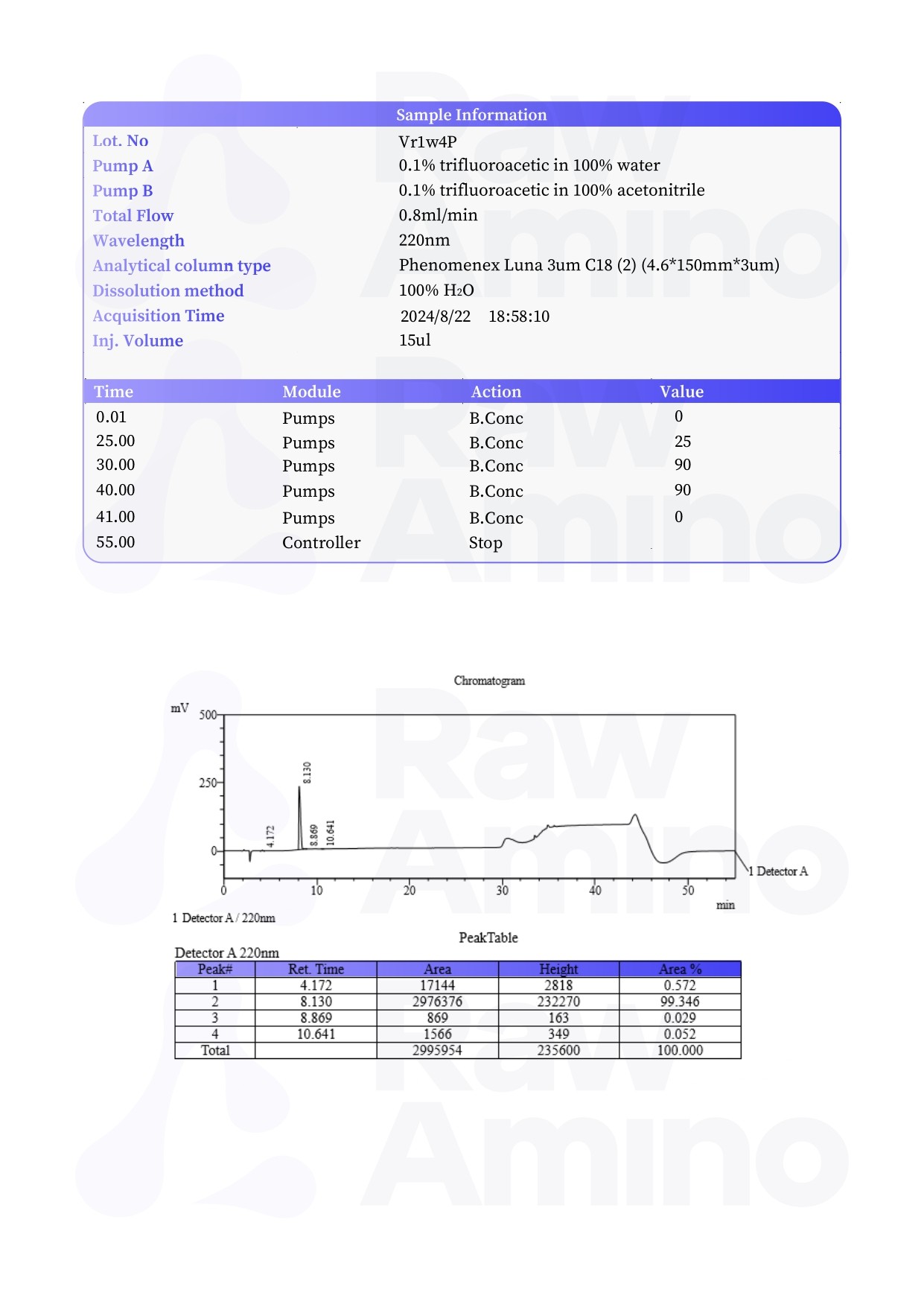
Cardiogen – 20MG
$60.00
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 8 | 5% | $57.00 |
| 9 + | 10% | $54.00 |
Scientific Overview of Cardiogen
Cardiogen is a synthetic tetrapeptide that has been studied in relation to cardiovascular and cellular processes. Research suggests it may be connected to fibroblast activity, which plays a role in scar formation and tissue repair. Investigations also indicate potential relevance to cellular proliferation, apoptosis, and protein expression.
Alternative Names: AEDR (Ala-Glu-Asp-Arg)
Cardiogen Studies and Research Data
Investigations on Cardiac Remodeling
Studies in experimental models propose that Cardiogen may be linked to the proliferation of cardiomyocytes, potentially influencing fibroblast growth and scar tissue development. Research also indicates a possible connection to reduced expression of p53 protein, which may be associated with apoptotic regulation in myocardial tissue.
Observations in Prostate Cell Models
Research into fibroblast-related signaling has considered Cardiogen among peptides that may alter the expression of factors associated with aging and cellular senescence. Findings suggest it may contribute to bringing altered signaling activity closer to levels seen in younger cell cultures, which has been discussed in relation to prostate research.
Explorations in Tumor Research
Cardiogen has also been examined in tumor cell studies. While in cardiac research it appears to be linked with reduced apoptosis, certain investigations into tumor models reported the opposite trend — suggesting possible increases in apoptosis and necrotic changes within tumor tissues. Researchers have hypothesized that this may occur through changes in tumor vasculature.
Cardiogen Research on Fibroblasts and Cytoskeletal Proteins
Laboratory studies involving embryonic fibroblasts indicate that Cardiogen may penetrate cellular compartments including the nucleus. Research suggests potential stimulation of cytoskeletal proteins such as actin, vimentin, and tubulin, along with nuclear proteins lamin A and C. These findings have been interpreted as possibly connected to enhanced transcriptional activity and altered metabolism.
Cardiogen Experimental Studies on Myocardial Damage
In murine models of myocardial injury, Cardiogen has been studied for possible roles in reducing tissue necrosis, preserving glycogen content, and supporting mitochondrial function. Findings also suggest a potential threefold decrease in mortality compared to control groups, with hypotheses linking this to reparative processes and cardiomyocyte metabolism.
Conclusion
Cardiogen is a synthetic peptide that has been investigated in contexts ranging from cardiac remodeling and fibroblast activity to tumor biology and cytoskeletal regulation. Research remains preliminary and primarily experimental, with findings suggesting possible roles in apoptosis regulation, protein expression, and tissue recovery processes. Further investigation is needed to clarify its full range of biological implications.
References
- Chalisova NI, Lesniak VV, Balykina NA, et al. [The effect of the amino acids and cardiogen on the development of myocard tissue culture from young and old rats]. Advances in Gerontology = Uspekhi Gerontologii. 2009;22(3):409-413. PMID: 20210190.
- Khavinson, V. K.h, Lin'kova, N. S., Polyakova, V. O., Kvetnoy, I. M., Benberin, V. V., D'yakonov, M. M., & Titkov, Y. S. (2012). Tetrapeptide H-Ala-Glu-Asp-Arg-OH stimulates expression of cytoskeletal and nuclear matrix proteins. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 153(4), 559–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-012-1766-9
- Kheĭfets OV, Poliakova VO, Kvetnoĭ IM. [Peptidergic regulation of the expression of signal factors of fibroblast differentiation in the human prostate gland in cell aging]. Advances in Gerontology = Uspekhi Gerontologii. 2010;23(1):68-70. PMID: 20586252.
- Levdik, N. V., & Knyazkin, I. V. (2009). Tumor-modifying effect of cardiogen peptide on M-1 sarcoma in senescent rats. Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine, 148(3), 433–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-010-0730-9
- Fedoreyeva, L. I., Kireev, I. I., Khavinson, V. K.h, & Vanyushin, B. F. (2011). Penetration of short fluorescence-labeled peptides into the nucleus in HeLa cells and in vitro specific interaction of the peptides with deoxyribooligonucleotides and DNA. Biochemistry. Biokhimiia, 76(11), 1210–1219. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297911110022
- Zakutskiĭ, A. N., Chalisova, N. I., & Subbotina, T. F. (2008). Bioorganicheskaia khimiia, 34(2), 149–159. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1068162008020015
- Khavinson, V., Linkova, N., Dyatlova, A., Kantemirova, R., & Kozlov, K. (2022). Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype of Cardiovascular System Cells and Inflammaging: Perspectives of Peptide Regulation. Cells, 12(1), 106.
Disclaimer:
The products mentioned are intended solely for laboratory research and in-vitro experimentation. They are not approved for human or animal use of any kind. All details provided are for educational purposes only. By purchasing from this site, you agree to comply with our Terms and Conditions.
Only logged in customers may leave a review.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.