
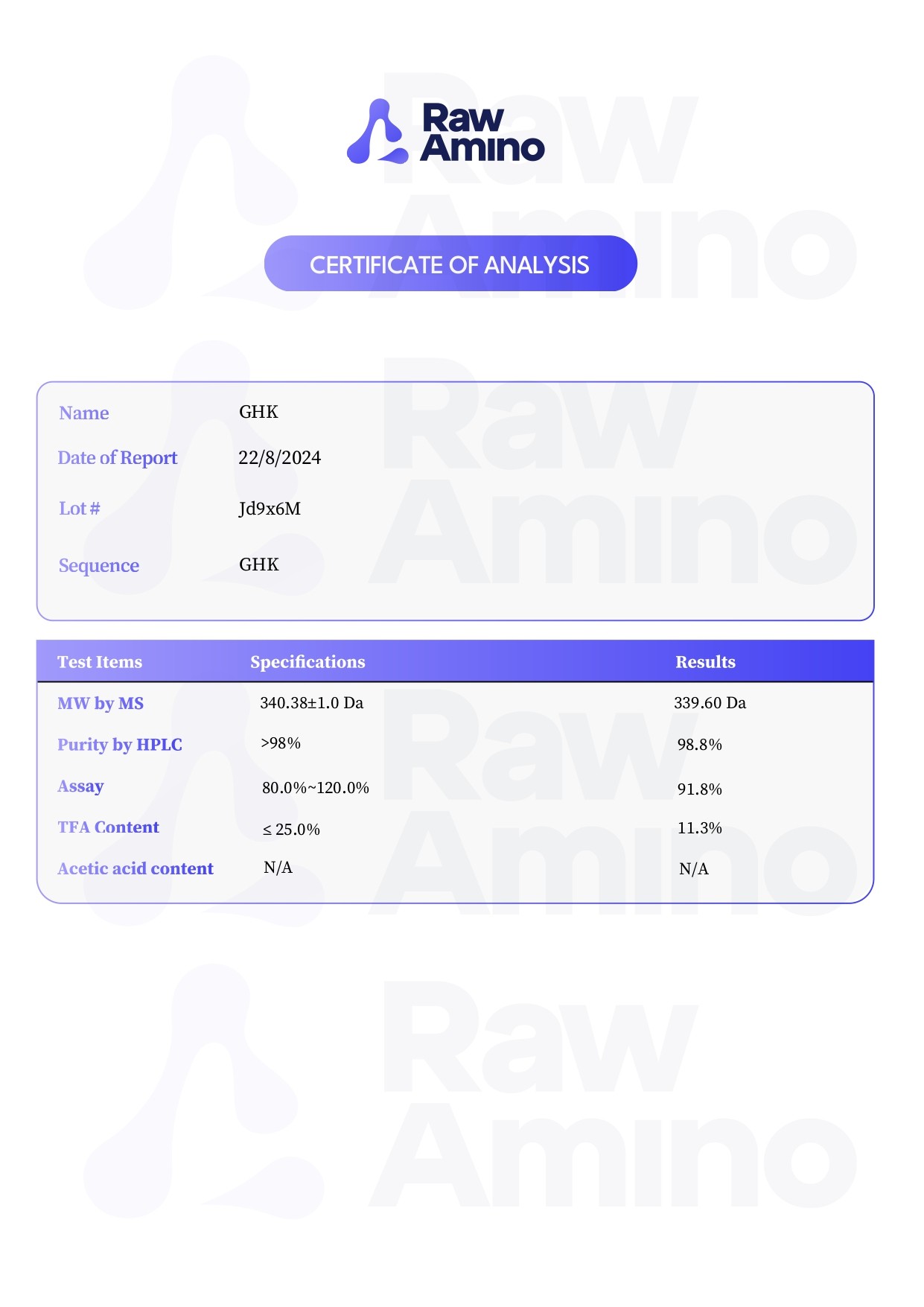
GHK Basic – 50MG
$51.00
Discount per Quantity
| Quantity | Discount | Price |
|---|---|---|
| 5 - 8 | 5% | $48.45 |
| 9 + | 10% | $45.90 |
Scientific Overview of GHK Basic Peptide
GHK (Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine) is a naturally occurring tripeptide that can be present with or without copper, often referred to as GHK-Cu when complexed. It has been identified in plasma and other tissues, and is thought to play a role in processes related to repair and regeneration. Over time, naturally occurring GHK levels appear to decline.
Alternative Names: Glycylhistidyllysine, GHK-Cu, Gly-His-Lys
GHK Basic Studies and Research Data
Research on Gene Regulation and DNA Repair
Investigations suggest that GHK may influence genes involved in DNA stability, antioxidant defenses, and repair pathways. Reports indicate that the peptide may stimulate antioxidant gene activity while lowering certain pro-oxidant signals, potentially contributing to genomic maintenance. Additional studies hypothesize that GHK may interact with reactive byproducts of lipid peroxidation, suggesting a possible role in protecting DNA integrity.
GHK Basic Exploration of Tissue Remodeling
Experimental work has examined GHK in the context of tissue recovery. In certain models, it appears to influence fibroblast activity, collagen production, and glycosaminoglycan synthesis. Researchers have proposed that these interactions may contribute to improved structural support and tissue repair. In respiratory models, GHK has been noted for potential involvement in gene expression changes linked to injury recovery.
Investigations into Inflammatory Pathways and Oxidative Stress
GHK has been studied for its relationship with inflammatory signaling and oxidative balance. Some evidence points toward possible reductions in oxidative stress markers, along with increased antioxidant enzyme activity. Research also suggests potential involvement in regulating cytokines such as IL-6 and pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK. Animal studies indicate that GHK may help lessen inflammatory responses in models of lung injury and oxidative stress.
GHK Basic Studies on Insulin-Related Genes and Cellular Longevity
Research indicates that GHK may modulate insulin and insulin-like gene expression, possibly impacting cellular lifespan. Data suggests that GHK can upregulate certain insulin-related genes while downregulating others, with links to studies proposing a relationship between reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling and delayed cellular aging.
Exploration of Fibrinogen Synthesis
GHK has been reported to influence fibrinogen production by altering expression of the beta chain, which is necessary for complete fibrinogen assembly. This disruption suggests a possible role in experimental models of coagulation and inflammation, opening avenues for further investigation into its regulatory capacity.
GHK Basic in Wound Recovery Research
Animal studies have explored GHK in relation to wound closure and collagen synthesis. In some models, GHK combined with external interventions such as laser exposure or dressing formulations appeared to accelerate wound contraction, vascular development, and epithelialization. The peptide has also been associated with increased antioxidant activity during tissue repair processes.
Research on Cancer-Related Gene Expression
Certain studies have examined the influence of GHK on tumor suppressor and DNA repair genes. Findings suggest that GHK may play a role in modifying gene expression patterns associated with suppression of metastasis-related pathways, though more research is needed to clarify its significance.
Conclusion
GHK has been widely studied in the context of gene expression, tissue repair, oxidative balance, and protein regulation. Research highlights its potential to influence biological pathways connected to repair, remodeling, inflammation, and cellular stability. While findings are promising, the data remains exploratory, and additional studies are required to establish the extent and relevance of these observations.
References
- Hong Y, Downey T, Eu KW, Koh PK, Cheah PY. A ‘metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications for possible therapeutics. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010 Feb;27(2):83-90.
- Miller, D. M., DeSilva, D., Pickart, L., & Aust, S. D. (1990). Effects of glycyl-histidyl-lysyl chelated Cu(II) on ferritin dependent lipid peroxidation. Advances in experimental medicine and biology, 264, 79–84.
- Dou Y, Lee A, Zhu L, Morton J, Ladiges W. The potential of GHK as an anti-aging peptide. Aging Pathobiol Ther. 2020 Mar 27;2(1):58-61.
- Campbell JD, McDonough JE, Zeskind JE, Hackett TL, Pechkovsky DV, Brandsma CA, Suzuki M, Gosselink JV, Liu G, Alekseyev YO, Xiao J, Zhang X, Hayashi S, Cooper JD, Timens W, Postma DS, Knight DA, Lenburg ME, Hogg JC, Spira A. A gene expression signature of emphysema-related lung destruction and its reversal by the tripeptide GHK. Genome Med. 2012 Aug 31;4(8):67.
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. The human tripeptide GHK-Cu in prevention of oxidative stress and degenerative conditions of aging. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:324832.
- Zhang, Q., Yan, L., Lu, J., & Zhou, X. (2022). Glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine-Cu2+ attenuates cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary emphysema and inflammation by reducing oxidative stress pathway. Frontiers in molecular biosciences, 9, 925700.
- Gul, N. Y., Topal, A., Cangul, I. T., & Yanik, K. (2008). The effects of tripeptide copper complex and helium-neon laser on wound healing in rabbits. Veterinary dermatology, 19(1), 7–14.
- Cass AE, Hill HA. Copper proteins and copper enzymes. Ciba Found Symp. 1980;79:71-91.
- Cebrián, J., Messeguer, A., Facino, R. M., & García Antón, J. M. (2005). New anti-RNS and -RCS products for cosmetic treatment. International journal of cosmetic science, 27(5), 271–278.
- Vitale G, Pellegrino G, Vollery M, Hofland LJ. ROLE of IGF-1 System in the Modulation of Longevity: Controversies and New Insights From a Centenarians’ Perspective. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 1;10:27.
- Pickart L, Margolina A. Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide in the Light of the New Gene Data. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 7;19(7):1987.
- Alven, S., Peter, S., Mbese, Z., & Aderibigbe, B. A. (2022). Polymer-Based Wound Dressing Materials Loaded with Bioactive Agents: Potential Materials for the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds. Polymers, 14(4), 724.
- Pickart L, Vasquez-Soltero JM, Margolina A. GHK and DNA: resetting the human genome to health. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:151479.
- Park, J. R., Lee, H., Kim, S. I., & Yang, S. R. (2016). The tri-peptide GHK-Cu complex ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Oncotarget, 7(36), 58405–58417.
Disclaimer:
The products mentioned are intended solely for laboratory research and in-vitro experimentation. They are not approved for human or animal use of any kind. All details provided are for educational purposes only. By purchasing from this site, you agree to comply with our Terms and Conditions.
Only logged in customers may leave a review.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.